1. Ultrasound Imaging Findings:
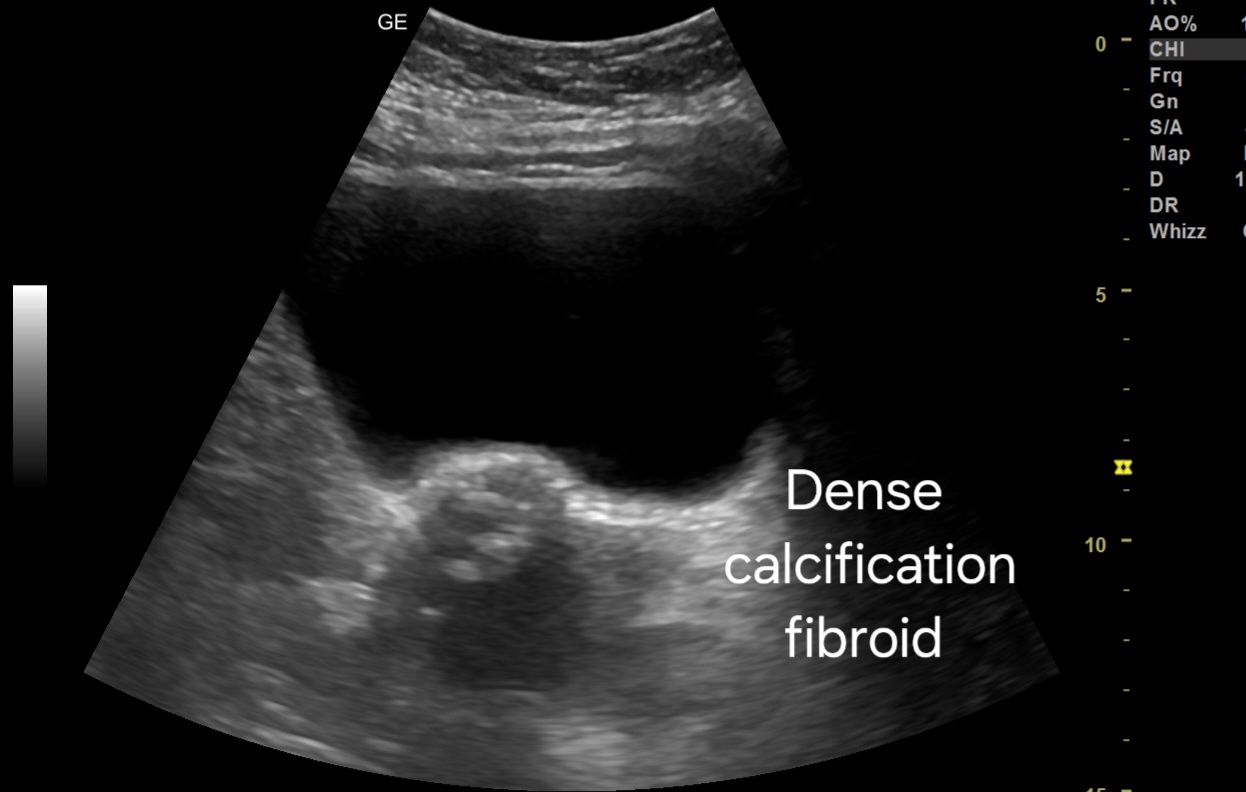
- Transabdominal Scan:
- Small fibroid located in the uterine wall.
- Severe calcification evident within the fibroid, causing acoustic shadowing.
- Hyperechoic appearance due to calcification, with reduced vascularity.
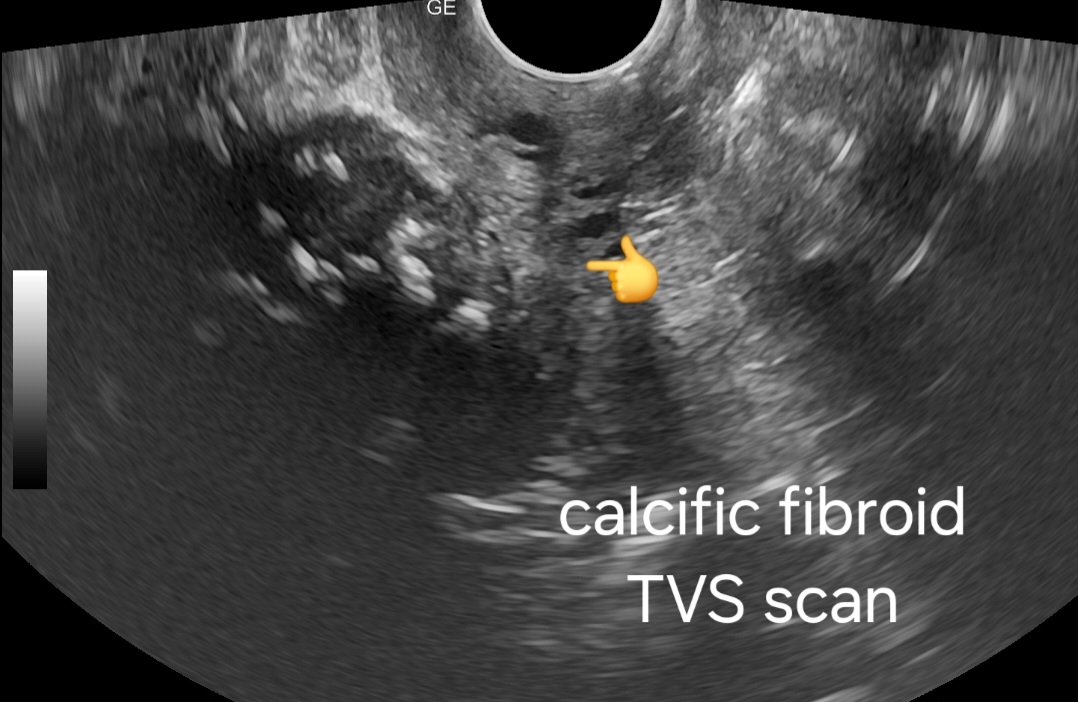
- Transvaginal Scan:
- Higher resolution imaging revealing finer details of fibroid morphology.
- Clearer visualization of calcification patterns within the fibroid.
- May identify any associated complications such as degeneration or necrosis.
2. Prognosis:
- Generally benign condition, especially in the absence of symptoms.
- Calcification often indicates long-standing fibroid presence.
- Rarely associated with malignancy or other complications.
- Prognosis favorable with appropriate management.
This ebook on Amazon Kindle may be useful:
3. Management:
- Observation:
- Asymptomatic patients may opt for conservative management.
- Regular follow-up with imaging to monitor any changes in size or symptoms.
- Symptomatic Management:
- Address symptoms such as pain or abnormal uterine bleeding with medication.
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) for pain relief.
- Hormonal therapy to regulate bleeding patterns.
- Surgical Intervention:
- Reserved for cases with severe symptoms or complications.
- Options include myomectomy or hysterectomy depending on patient preference and clinical indication.
- Considerations include patient age, overall health, and desire for fertility preservation.
Conclusion:
Severe calcification of a small fibroid in elderly female patients presents a unique imaging challenge but is generally associated with a favorable prognosis. Management strategies range from observation to surgical intervention, depending on the patient's symptoms and preferences.
---
Feel free to adjust or add any details as needed!




No comments:
Post a Comment