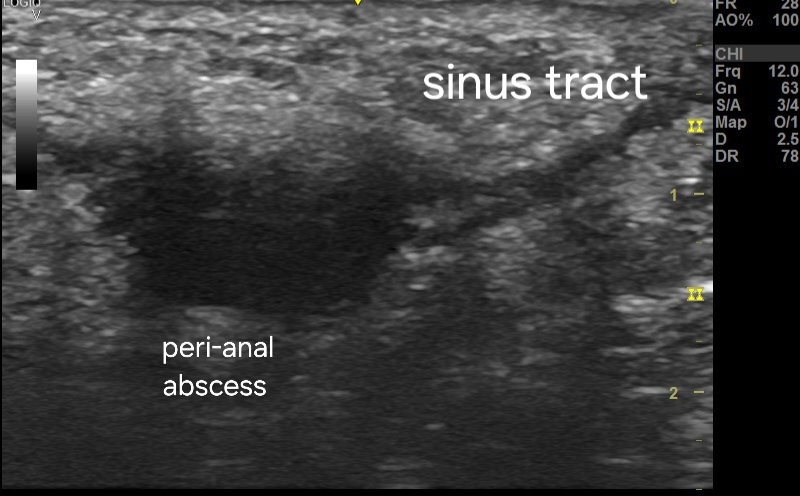
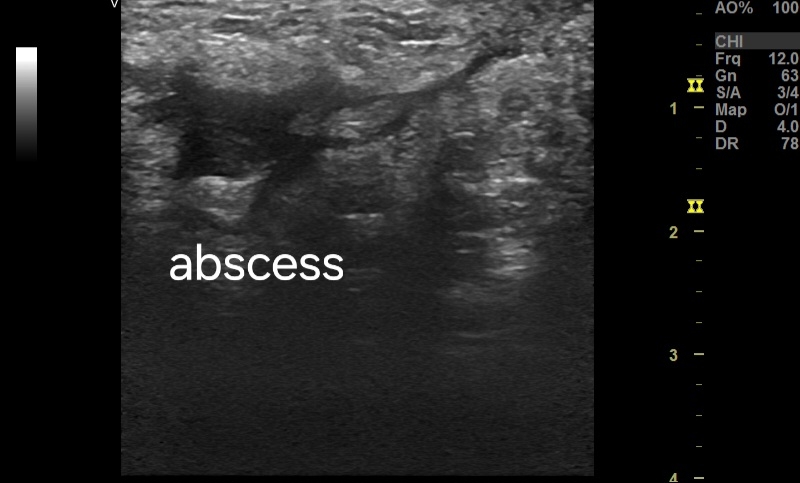
**Ultrasound features:
* Size: 1.5 cm, typically irregular and oval in shape.
* Margin: Hyperechoic rim surrounding a hypoechoic center.
* Internal echoes: Hypoechoic due to fluid and debris within the abscess.
* Sinus tract: Appears as a hypoechoic tract extending from the abscess, potentially connecting to the skin surface.
*Doppler flow: Absent within the abscess itself, but is present around the margins.
Images:
For more visit:
**Prognosis:
* Generally good with early diagnosis and prompt treatment.
* Delayed treatment can lead to complications like extension of infection, fistula formation, and cellulitis.
* Recurrence rates can be high, especially in patients with underlying inflammatory bowel disease.
**Management:
* *Incision and drainage: The mainstay of treatment, usually guided by ultrasound for accuracy.
*Antibiotic therapy: Broad-spectrum antibiotics to cover potential skin and gut flora.
* Pain management: Medications and Sitz baths for pain relief.
* Dietary modifications: High-fiber diet to promote stool regularity and reduce straining.
* Fistula management: Additional procedures like fistulotomy or fibrin sealant injection may be needed for complex fistulas.
**Additional notes:
* Ultrasound is a readily available, non-invasive, and relatively inexpensive imaging modality for peri-anal abscesses.
* In some cases, MRI may be needed for further evaluation, especially if the abscess is complex or there is suspicion of Crohn's disease involvement.
* Prognosis and management depend on individual factors like abscess size, presence of fistula, and underlying medical conditions.


No comments:
Post a Comment