#Clinical Context
1. Patient Presentation:
- Symptom: Pain associated with diabetic foot.
- Relevance: Diabetic patients are at high risk for peripheral arterial disease (PAD).
#Doppler Ultrasound Findings
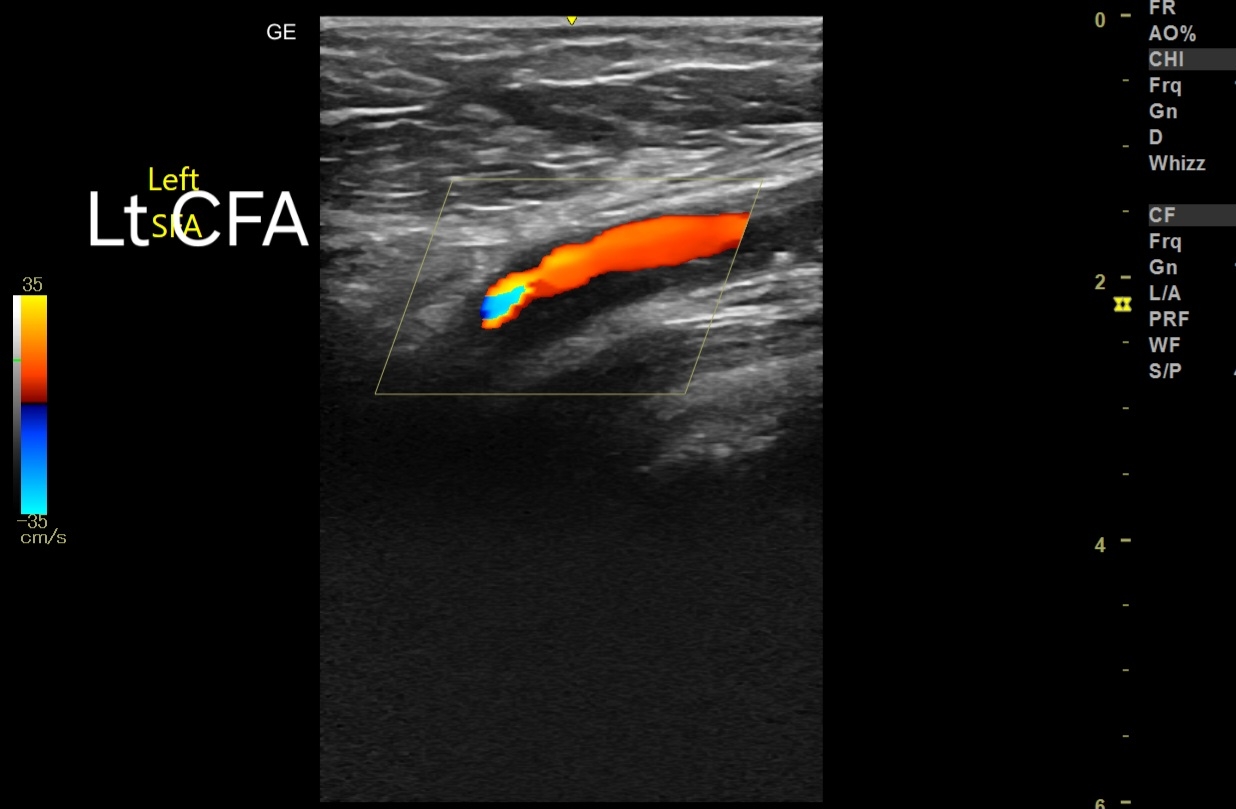
1. Common Femoral Artery (CFA):
- Peak Systolic Velocity (PSV): 140 cm/s.
- Interpretation: Elevated PSV suggesting focal stenosis.
- Implication: Likely significant stenosis at the site, given that normal PSV in the CFA is usually less than 125 cm/s.
2. Superficial Femoral Artery (SFA):
- Flow Velocity: Very low, Tardus parvus waveform
- Interpretation: Indicates possible severe stenosis or occlusion proximal to the point of measurement.
In addition, diffuse stenotic disease present
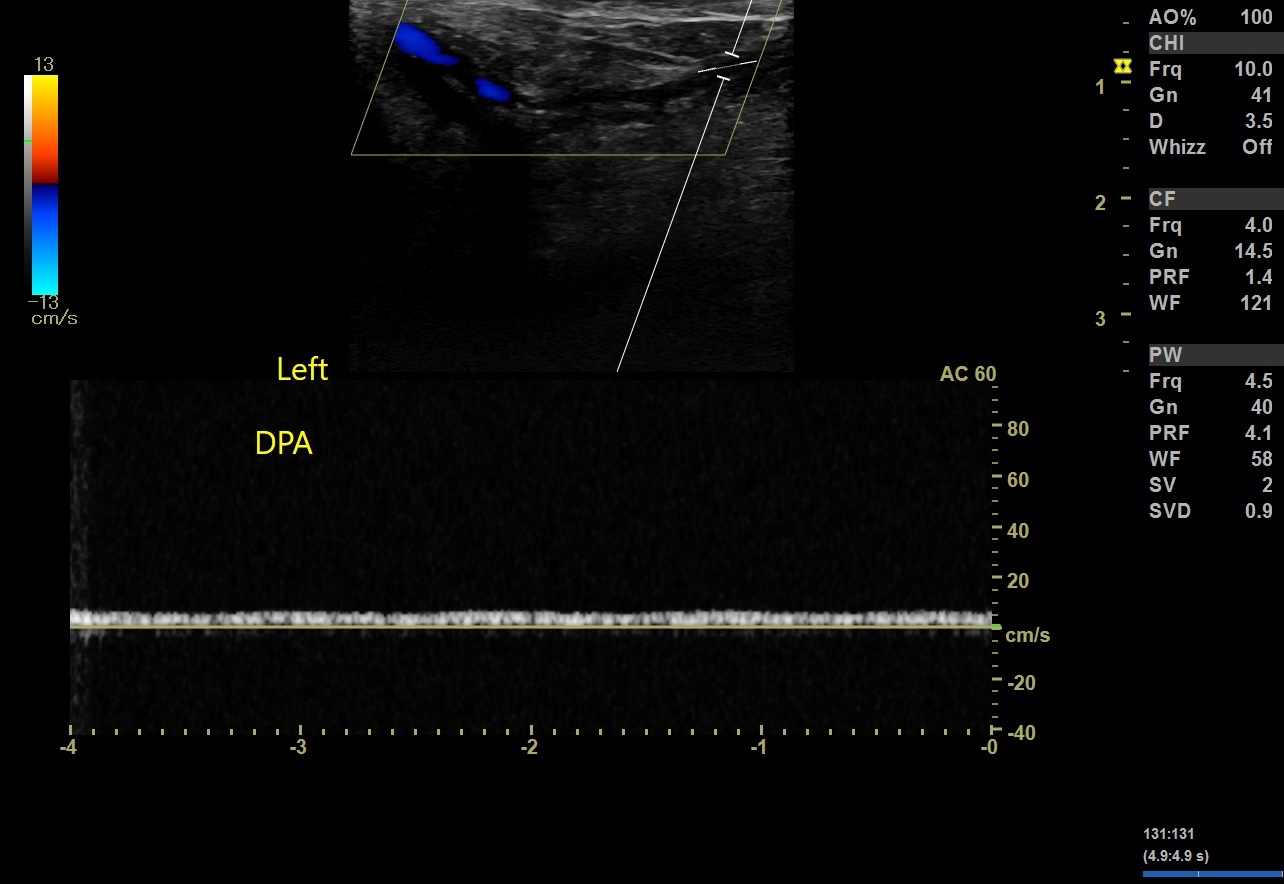
3. Flow Pattern (Tardus Parvus):
- Observed In: SFA downwards to popliteal artery, anterior tibial artery (ATA), posterior tibial artery (PTA), and dorsalis pedis artery (DPA).
- Description: Tardus parvus is characterized by a delayed systolic upstroke and reduced peak velocity.
- Implication: Suggests a proximal high-grade stenosis or occlusion impacting distal arterial flow.
#Diagnostic Interpretation
1. Proximal Stenosis/Occlusion:
- Significant stenosis noted at the CFA with PSV of 140 cm/s.
- Likely contributing to compromised blood flow distally, as evidenced by low velocities and tardus parvus waveform in SFA and beyond.
2. Distal Perfusion:
- Poor perfusion in the distal arteries (SFA, popliteal, ATA, PTA, DPA).
- Indicative of critical limb ischemia, which is concerning in the context of a diabetic foot due to the risk of non-healing ulcers and potential for limb loss.
#Clinical Implications
1. Management Considerations:
- Immediate: Vascular consultation for potential revascularization (angioplasty, stenting, or bypass surgery).
- Long-term: Aggressive management of diabetes and PAD risk factors (smoking cessation, cholesterol management, antiplatelet therapy).
2. Monitoring and Follow-up:
- Close follow-up with repeat imaging to monitor the effectiveness of interventions and disease progression.
- Regular foot care and monitoring to prevent complications associated with diabetic foot.
#Summary
- The findings suggest significant stenosis at the CFA with downstream severe impairment of arterial flow in the lower limb.
- Tardus parvus waveform from the SFA down to the foot arteries is indicative of a high-grade proximal obstruction.
- Prompt vascular intervention is warranted to restore adequate perfusion and prevent further complications in a diabetic patient.