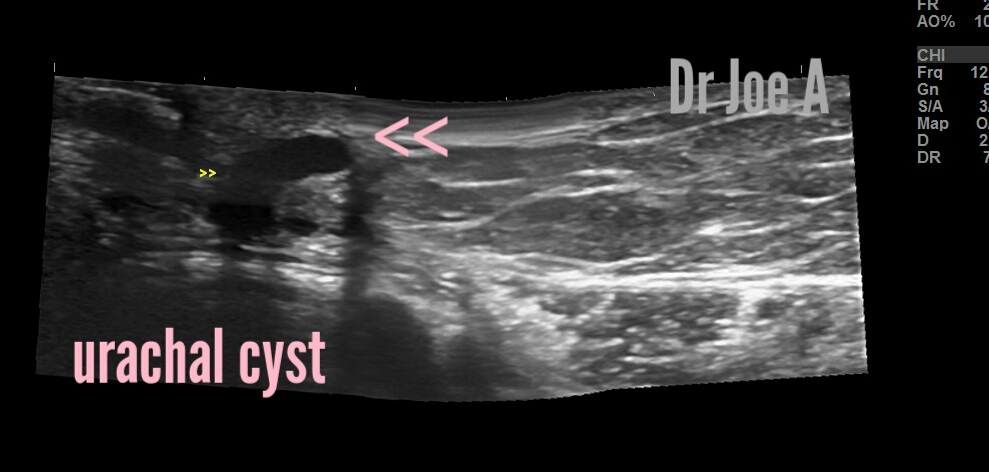
Ultrasound imaging was done and showed these findings:
A diagnosis of urachal cyst was made.
Urachal Cyst: Diagnosis, Prognosis, and Management
What are urachal cysts?
Urachal cysts are rare developmental abnormalities that arise from the urachus, a structure that connects the bladder to the umbilicus during fetal development. These cysts can occur in both children and adults, and are more common in males than in females. Here, we will discuss the case of a 24-year-old female who was diagnosed with a urachal cyst.
Case Presentation
A 24-year-old female presented with abdominal discomfort and a 1 cm-sized cyst within the abdominal wall just to the left of the umbilicus. She had no significant past medical or surgical history, and no family history of similar symptoms. An ultrasound was performed, which showed an elongated cystic lesion just to the left of the umbilicus, consistent with a urachal cyst. The patient was referred for further evaluation and management.
Ultrasound Findings:
The ultrasound findings in this case are consistent with a urachal cyst. The following were the characteristics of the cyst on ultrasound:
1. An elongated cystic lesion just to the left of the umbilicus within the abdominal wall.
2. The cyst had well-defined margins, and was hypoechoic, meaning it appeared darker than the surrounding tissue.
3. The cyst was fluid-filled and contained no solid components.
Differential Diagnosis:
Urachal cysts are rare congenital abnormalities that arise from the urachus, a remnant of the allantois that connects the bladder to the umbilicus during fetal development. The chief differential diagnoses in cyst near the umbilicus in this 24-year-old female include:
1. Umbilical hernia: This occurs when part of the abdominal contents protrude through a weakened area around the umbilicus. Less likely as there is no external swelling visible on coughing.
2. Omphalitis: This is an infection of the umbilicus and surrounding tissues. It can occur in infants, but can also occur in adults.
3. Lipoma: This is a benign growth of fatty tissue that can occur anywhere on the body, including near the umbilicus. Less likely as lipoma is solid while this case shows a cystic lesion.
4. Fibroma: This is a benign growth of fibrous tissue that can occur near the umbilicus. Not likely as fibroma is a solid lesion.
5. Dermoid cyst: This is a type of cyst that contains hair, skin, and other tissues. They can occur anywhere on the body, including near the umbilicus. This is a possible important differential diagnosis.
6. Epigastric hernia: This occurs when part of the abdominal contents protrude through a weak spot in the abdominal wall above the umbilicus. There was no external mass visible in our case. Hence, excluded.
7. Carcinoma of the urachus: This is a rare form of cancer that can arise from the urachus. It can cause a mass near the umbilicus, but is more common in older individuals. Very rare and not possible in this case.
Final diagnosis: urachal cyst near umbilicus.
Prognosis:
The prognosis for a urachal cyst is generally good. In most cases, the cysts are benign and do not cause any symptoms. However, in rare cases, the cysts may become infected or rupture, leading to abdominal pain, fever, and other complications. If left untreated, the cysts can also grow larger and cause discomfort or obstructive symptoms.
Management
The management of a urachal cyst depends on the size and symptoms of the cyst, as well as the age and overall health of the patient. In most cases, small cysts that are asymptomatic do not require any treatment, and can be monitored with regular imaging tests. However, larger cysts or cysts that cause symptoms may require surgical intervention.
The following are the management options for urachal cysts:
1. Observation: Small, asymptomatic cysts can be monitored with regular imaging tests to ensure that they are not growing or causing any problems.
2. Antibiotics: If the cyst becomes infected, antibiotics may be prescribed to treat the infection.
3. Surgical intervention: Larger cysts or cysts that cause symptoms may require surgical removal. This can be done using minimally invasive techniques or open surgery, depending on the size and location of the cyst.
Conclusion
Urachal cysts are rare developmental abnormalities that can occur in both children and adults. They are generally benign, but can become symptomatic or lead to complications if left untreated. In the case of the 24-year-old female described above, an ultrasound showed an elongated cystic lesion just to the left of the umbilicus, consistent with a urachal cyst. The management of urachal cysts depends on the size and symptoms of the cyst, and may include observation, antibiotics, or surgical intervention.
For more details visit:







No comments:
Post a Comment