#ParathyroidAdenoma #NeckUltrasound #ColorDoppler #Hypercalcemia
Ultrasound imaging
Tuesday, May 13, 2025
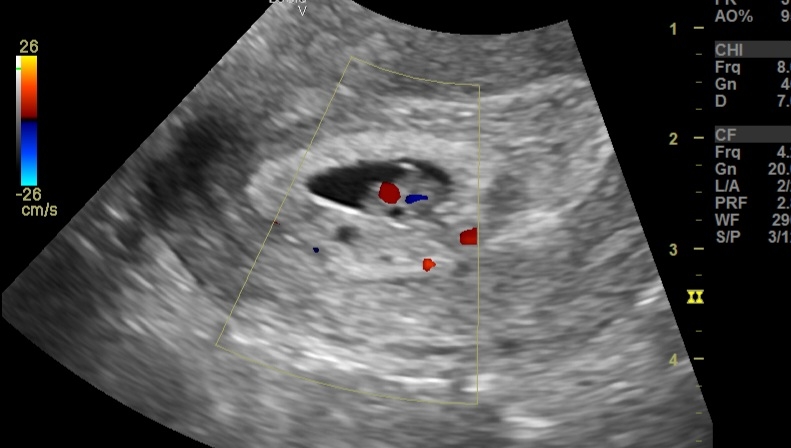
Parathyroid adenoma
Monday, December 9, 2024
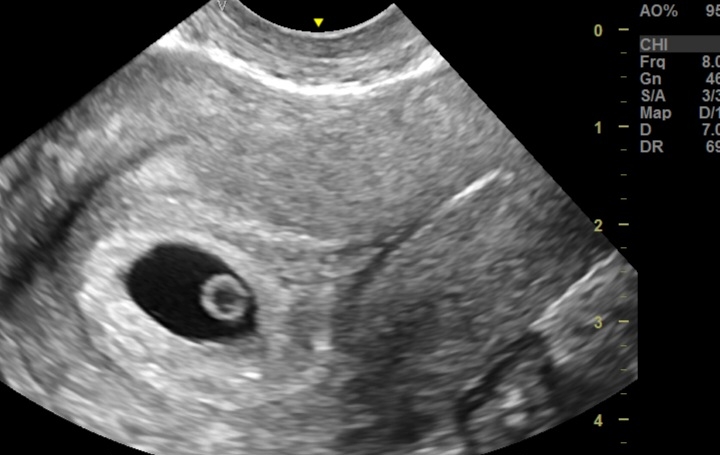
Normal TVS Ultrasound and Color Doppler Findings at 6 Weeks of Pregnancy: A Quick Guide
Normal Ultrasound and Color Doppler Findings at 6 Weeks Pregnancy (TVS)
1. Gestational Sac: Round/oval, located within the uterine cavity, mean sac diameter ~10-15 mm.
2. Yolk Sac: Visible within the gestational sac, measuring ~2-5 mm.
3. Fetal Pole: Crown-rump length (CRL) ~2-6 mm, adjacent to the yolk sac.
4. Cardiac Activity: Detectable, fetal heart rate ~90-110 bpm.
5. Myometrium: Normal echotexture, no abnormal masses or collections.
6. Adnexa: Normal ovaries and absence of ectopic pregnancy.
7. Color Doppler: Demonstrates blood flow within the decidua and corpus luteum, if visible.
8. Amniotic Cavity: Beginning to form, visible as a small space around the fetal pole.
#6WeeksPregnancy #Ultrasound #TVSScan #PregnancyUltrasound #EarlyPregnancy #ColorDoppler #FetalDevelopment #GestationalSac #YolkSac #FetalHeartbeat #ObstetricImaging #PregnancyCare
Saturday, November 16, 2024
Ultrasound Insights into Azoospermia: Diagnosing Testicular Hypoplasia and CBAVD
An ultrasound scan of a male patient with infertility and azoospermia revealed the following:
1. Testes:
Small testes with volume <2 cc, significantly below the normal range (12–25 cc).
Poor vascularity on color Doppler, indicating reduced blood flow.
2. Bilateral Grade 1 Varicocele:
Mild dilation of the pampiniform plexus.
3. Transrectal Ultrasound (TRUS):
Small seminal vesicles, potentially hypoplastic.
Possibly absent vas deferens, indicated by its non-visualization.
Normal prostate with no abnormalities detected.
Differential Diagnoses:
1. Congenital Bilateral Absence of the Vas Deferens (CBAVD):
Commonly associated with cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR) gene mutations.
May present with hypoplastic or absent seminal vesicles and azoospermia.
2. Primary Testicular Failure (Hypogonadism):
Testicular atrophy and poor vascularity may indicate failure of spermatogenesis.
Causes include genetic syndromes like Klinefelter syndrome, previous orchitis, or trauma.
3. Y-Chromosome Microdeletions:
Specifically in the AZF region, leading to testicular dysfunction and azoospermia.
4. Obstructive Azoospermia:
Secondary to structural anomalies like CBAVD or scarring.
5. Secondary Hypogonadism:
If associated with pituitary or hypothalamic dysfunction, but this is less likely given the absent vas deferens.
---
Most Likely Diagnosis
Congenital Bilateral Absence of the Vas Deferens (CBAVD):
The combination of small testes, poorly vascular testes, azoospermia, small seminal vesicles, and absent vas deferens strongly suggests CBAVD.
---
Prognosis
Fertility:
Natural conception is not possible.
Sperm retrieval techniques (e.g., testicular sperm extraction, TESE) combined with intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI) may be viable for fathering biological children.
Overall Health:
Usually, no systemic health effects unless associated with CFTR mutations.
If CFTR-related, patients may have subclinical or overt cystic fibrosis symptoms (e.g., recurrent respiratory infections, pancreatitis).
---
Management
1. Diagnostic Confirmation:
Genetic testing for CFTR mutations and Y-chromosome microdeletions.
Hormonal evaluation (FSH, LH, testosterone) to differentiate primary vs. secondary causes.
2. Fertility Options:
Referral to a fertility specialist.
Consideration of TESE with ICSI.
Partner evaluation for CFTR carrier status if CFTR mutation is confirmed.
3. Counseling:
Address psychological and emotional aspects of azoospermia.
Genetic counseling if hereditary factors are identified.
4. Monitoring:
Regular follow-ups for any complications or related health concerns (e.g., cystic fibrosis symptoms).
#Azoospermia
#TesticularHypoplasia
#CBAVD
#MaleInfertility
#UltrasoundDiagnosis
#ReproductiveHealth
#FertilityCare
Tuesday, November 12, 2024
Long section ultrasound view normal Gastroesophageal junction
Tuesday, September 3, 2024
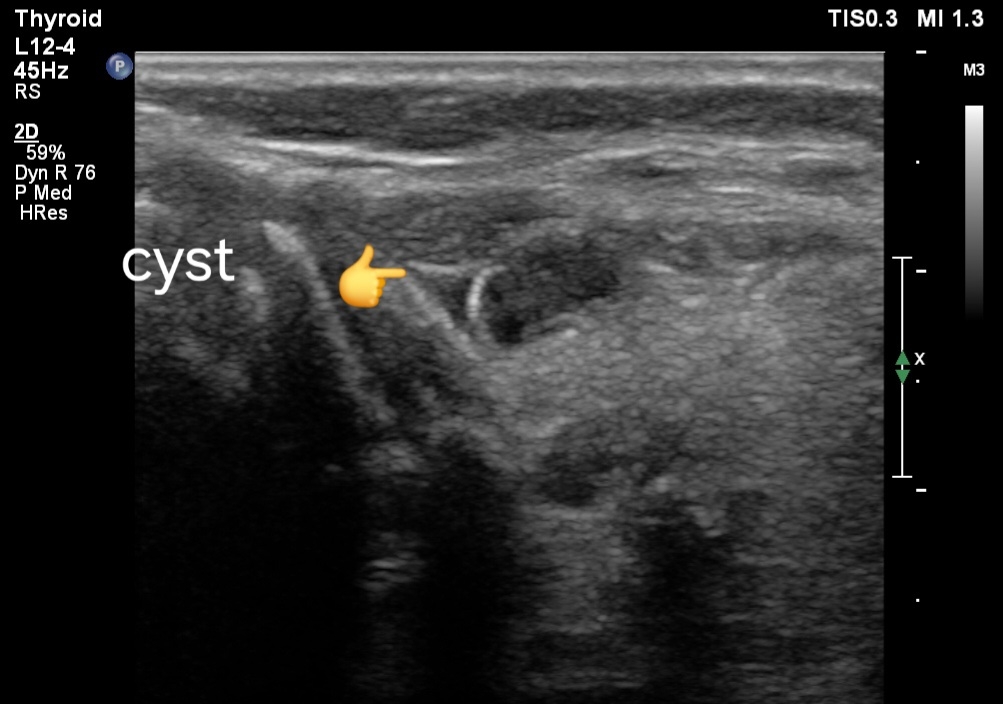
Multiple simple cysts of thyroid, ultrasound imaging
Ultrasound and Color Doppler Imaging Findings:
1. Ultrasound Findings:
- Cystic Appearance: The thyroid shows multiple small anechoic or hypoechoic areas corresponding to cysts, predominantly in the left lobe. These cysts are round or oval, with well-defined borders and no internal echoes if simple.
- Size:The cysts may vary in size but are typically small, often less than 1 cm in diameter.
- Location: The cysts are clustered in specific regions.
- Internal Features: If the cysts are complex, they may contain internal debris, septations, or a mixture of solid and cystic components.
- Thyroid Parenchyma: The surrounding thyroid tissue may appear normal or show signs of background thyroid disease, such as Hashimoto's thyroiditis, which might present as a heterogeneous echotexture.
2. Color Doppler Findings:
- Vascularity: Simple cysts usually show no internal vascularity on color Doppler imaging. If the cysts have solid components or are complex, there may be some peripheral vascularity but generally no significant internal flow.
- Surrounding Tissue: The surrounding thyroid parenchyma may exhibit normal or increased vascularity, particularly if associated with inflammatory or other thyroid pathologies.
Prognosis:
- Simple Cysts: Simple thyroid cysts are typically benign with an excellent prognosis. They are usually asymptomatic and may not require any intervention unless they grow or cause symptoms.
- Complex Cysts: The presence of solid components or other complex features warrants further evaluation, as there may be a risk of malignancy, though most cystic lesions remain benign.
- Multiple Cysts: Having multiple cysts, particularly if small and simple, is generally not a cause for concern. However, ongoing monitoring is often recommended.
Management:
- Observation: Most small, simple cysts are managed with regular follow-up and ultrasound monitoring to check for any changes in size or characteristics.
- Fine-Needle Aspiration (FNA): If a cyst is complex, symptomatic, or has suspicious features, FNA may be performed to obtain a sample for cytological examination.
- Surgery: Surgical intervention is rarely needed unless the cysts are large, symptomatic, or have suspicious features suggesting malignancy.
- Medical Management: If the cysts are associated with underlying thyroid disease (e.g., Hashimoto's thyroiditis), management of the underlying condition may be necessary.
Read about Thyroid disease and management:
Thyroid disease, get that scan (India)
Thyroid disease, get that scan ( USA 🇺🇸, Europe 🇪🇺)
#ThyroidUltrasound
#DopplerImaging
#ThyroidCare
#ThyroidDiagnosis
#RadiologyBlog
#CysticLesions
#ThyroidManagement
#ThyroidPrognosis
#ThyroidDisease
#MedicalUltrasound
Thursday, August 15, 2024
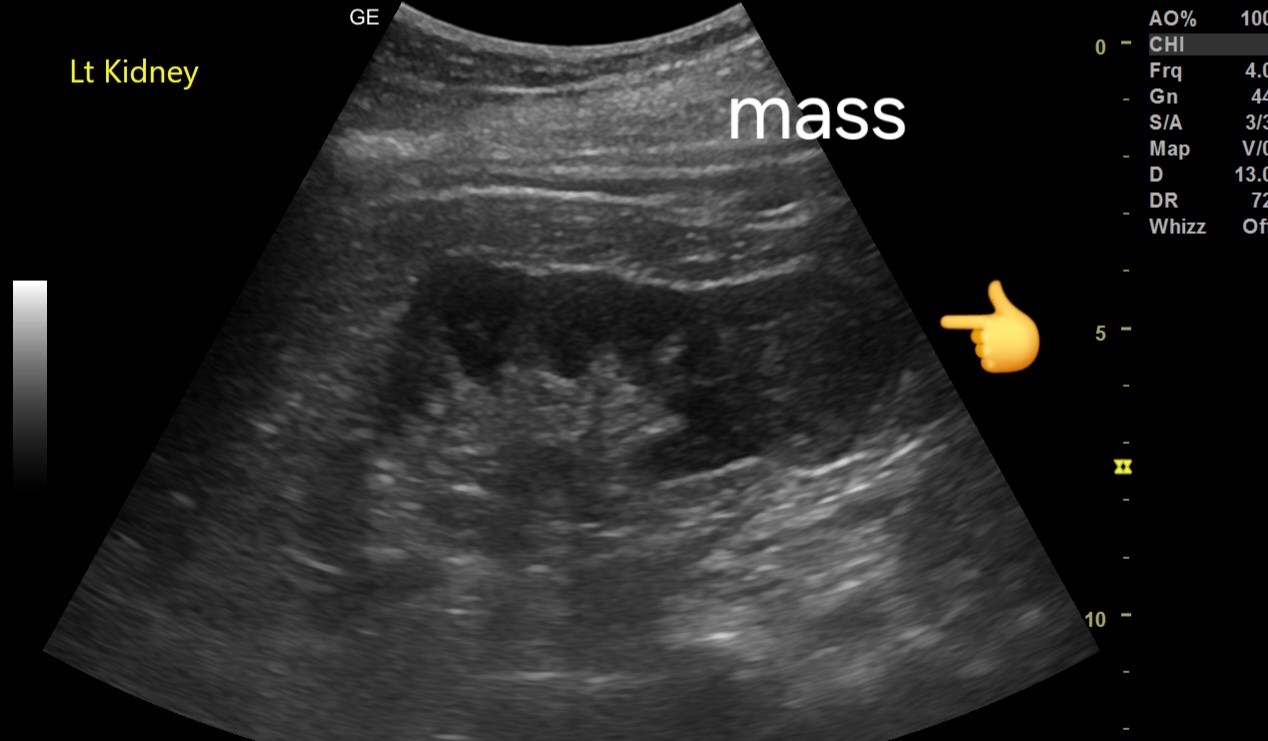
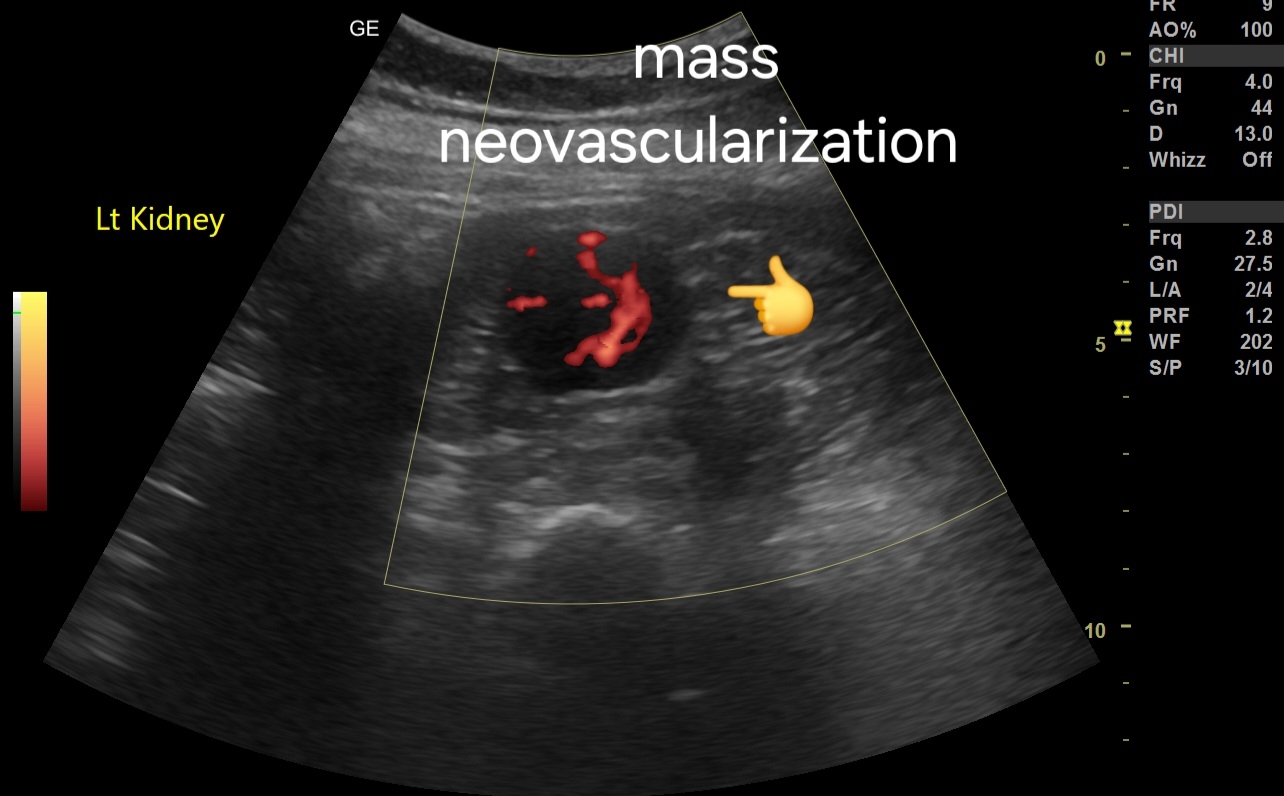
Sonography in early Renal cell carcinoma
Ultrasound Imaging Findings:
- Location and Size: Mass located in the lower pole of the kidney, measuring 3.5 cm.
- Echotexture: Mildly inhomogeneous echotexture, with areas of mixed echogenicity.
- Margins: Poorly defined, irregular margins, suggestive of malignancy.
- Internal Characteristics: May show subtle areas of necrosis or hemorrhage, contributing to the inhomogeneity.
Color Doppler Imaging Findings:
- Neovascularization: Presence of abnormal, disorganized blood vessels within the mass, characteristic of neovascularization.
- Vascular Pattern: The mass demonstrates a hypervascular pattern with multiple feeding vessels.
Spectral Doppler Imaging Findings:
- Venous Flow Pattern: A vessel within the mass exhibits a venous flow pattern on spectral Doppler, which is atypical and may suggest arteriovenous shunting.
- Low Resistive Index (RI): A low resistive index may be noted, consistent with the hypervascularity of the mass.
Suspected Diagnosis:
- Renal Cell Carcinoma (RCC): The combination of ultrasound and Doppler findings, along with the CT scan, raises a strong suspicion for renal cell carcinoma.
See more at:
Also:
#Prognosis:
- Stage-Dependent: Prognosis varies with the stage of the disease; localized RCC generally has a favorable prognosis, while advanced or metastatic cases have a poorer outlook.
- Aggressive Potential: Given the neovascularization and poorly defined margins, there may be a higher risk of local invasion and metastasis.
#Management:
1. Further Imaging: Contrast-enhanced CT or MRI is essential for staging and better characterization of the mass.
2. Biopsy: Consider percutaneous biopsy to obtain a definitive histological diagnosis.
3. Surgical Treatment: Partial or radical nephrectomy, depending on the tumor size, location, and patient's overall condition.
4. Ablation: For small, localized tumors or in non-surgical candidates, thermal ablation might be considered.
5. Systemic Therapy: Advanced cases may require targeted therapies or immunotherapy.
6. Follow-Up: Regular imaging to monitor for recurrence or metastasis is crucial.
Thursday, July 4, 2024
Ultrasound Imaging of Gallbladder Sludge Mimicking a Mass with Concurrent Cholelithiasis
Case Presentation:
A 45-year-old female presented with right upper quadrant abdominal pain. Ultrasound examination revealed a heterogeneous hyperechoic lesion in the gallbladder, initially suspected to be a mass. Further evaluation revealed the presence of sludge and a gallbladder calculus.
Discussion:
Gallbladder sludge can mimic a mass on ultrasound imaging, leading to potential misdiagnosis. The presence of a concurrent gallstone in this case further complicated the diagnosis. However, careful evaluation of the lesion's morphology and movement on ultrasound helped confirm the diagnosis of sludge and a gallbladder calculus.
No vascularity was present in the lesion.
Conclusion:
This case highlights the importance of careful evaluation of gallbladder pathology on ultrasound imaging to avoid potential misdiagnosis. The presence of sludge and gallstones can mimic more sinister pathology, emphasizing the need for a thorough and experienced evaluation.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)