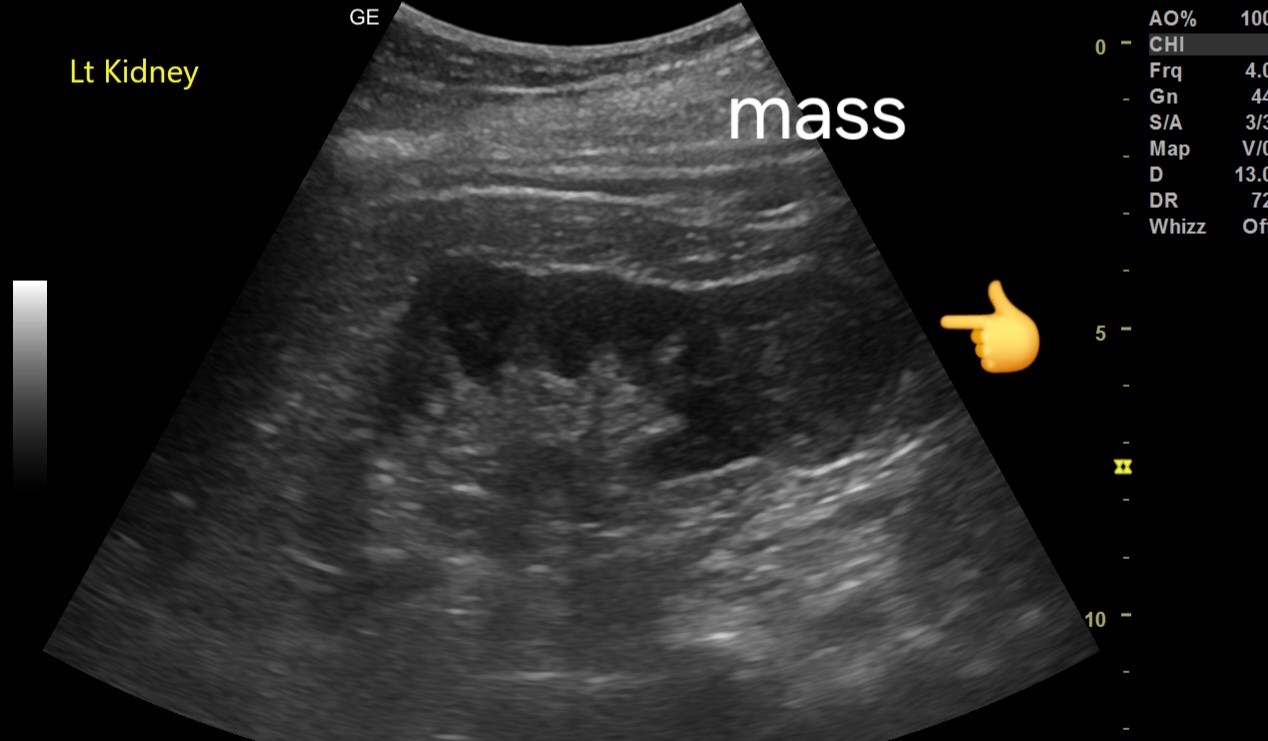
- Location and Size: Mass located in the lower pole of the kidney, measuring 3.5 cm.
- Echotexture: Mildly inhomogeneous echotexture, with areas of mixed echogenicity.
- Margins: Poorly defined, irregular margins, suggestive of malignancy.
- Internal Characteristics: May show subtle areas of necrosis or hemorrhage, contributing to the inhomogeneity.
Color Doppler Imaging Findings:
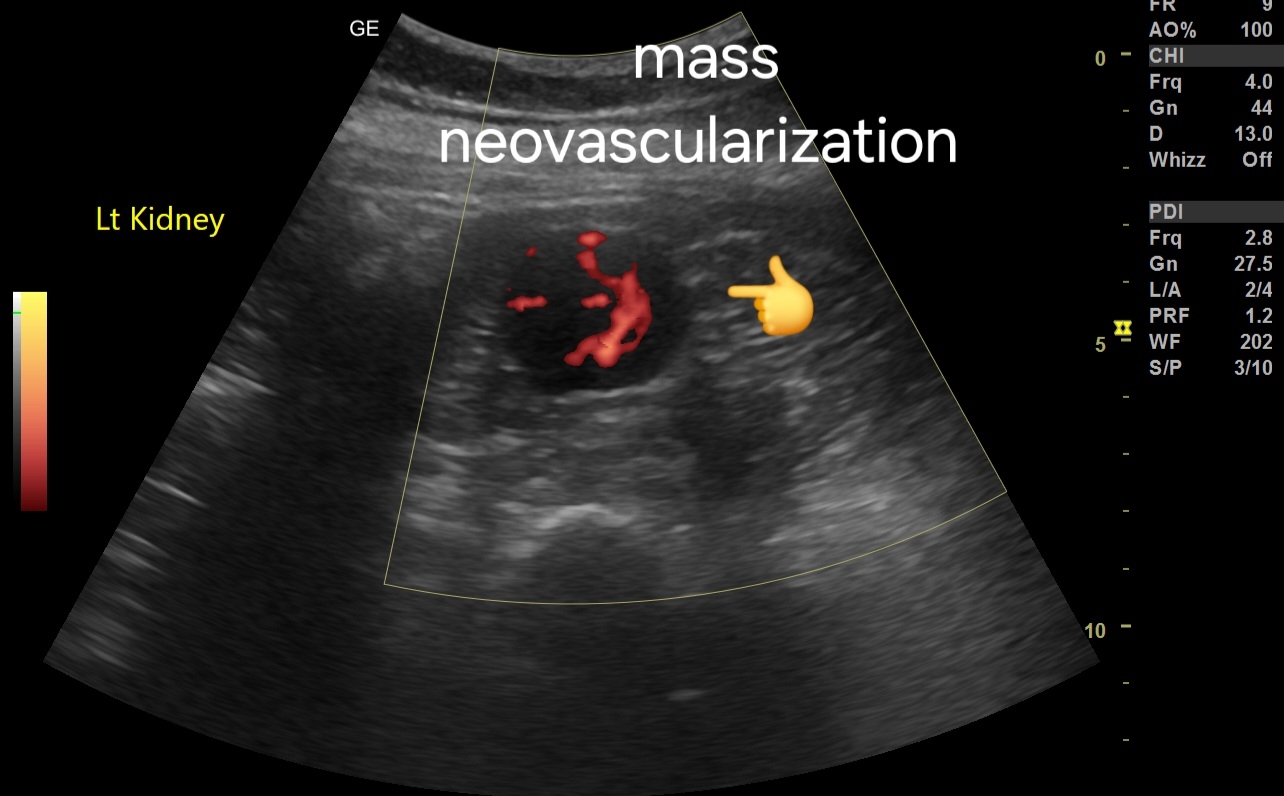
- Neovascularization: Presence of abnormal, disorganized blood vessels within the mass, characteristic of neovascularization.
- Vascular Pattern: The mass demonstrates a hypervascular pattern with multiple feeding vessels.
Spectral Doppler Imaging Findings:
- Venous Flow Pattern: A vessel within the mass exhibits a venous flow pattern on spectral Doppler, which is atypical and may suggest arteriovenous shunting.
- Low Resistive Index (RI): A low resistive index may be noted, consistent with the hypervascularity of the mass.
Suspected Diagnosis:
- Renal Cell Carcinoma (RCC): The combination of ultrasound and Doppler findings, along with the CT scan, raises a strong suspicion for renal cell carcinoma.
See more at:
Also:
#Prognosis:
- Stage-Dependent: Prognosis varies with the stage of the disease; localized RCC generally has a favorable prognosis, while advanced or metastatic cases have a poorer outlook.
- Aggressive Potential: Given the neovascularization and poorly defined margins, there may be a higher risk of local invasion and metastasis.
#Management:
1. Further Imaging: Contrast-enhanced CT or MRI is essential for staging and better characterization of the mass.
2. Biopsy: Consider percutaneous biopsy to obtain a definitive histological diagnosis.
3. Surgical Treatment: Partial or radical nephrectomy, depending on the tumor size, location, and patient's overall condition.
4. Ablation: For small, localized tumors or in non-surgical candidates, thermal ablation might be considered.
5. Systemic Therapy: Advanced cases may require targeted therapies or immunotherapy.
6. Follow-Up: Regular imaging to monitor for recurrence or metastasis is crucial.